Understanding ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a group of rare autoimmune disorders in which the immune system attacks the body’s small blood vessels, causing inflammation and damage. “ANCA” refers to anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies — autoantibodies that play a central role in driving the disease.
The most common forms include:
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)
AAV can affect many organs — including the kidneys, lungs, skin, nerves, and sinuses — and may be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Symptoms vary widely but may include persistent sinus inflammation, coughing up blood, skin rashes, nerve pain, fatigue, and kidney failure.
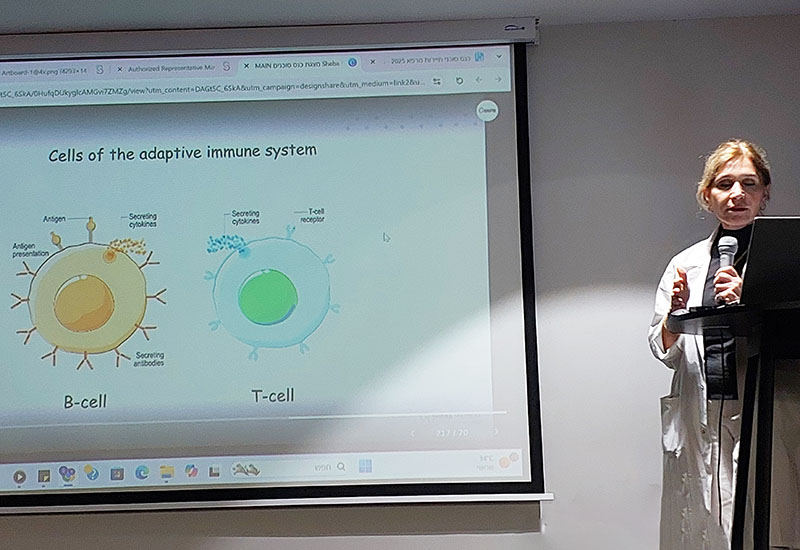
Prof. Lidar Presents on CAR-T Therapy for Rheumatologic Diseases
Current Treatments – and Their Limitations
Standard therapy for ANCA vasculitis usually involves:
- High-dose corticosteroids to rapidly reduce inflammation
- Immunosuppressants such as cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, or mycophenolate
- Biologic therapies like rituximab (MabThera) for B-cell depletion
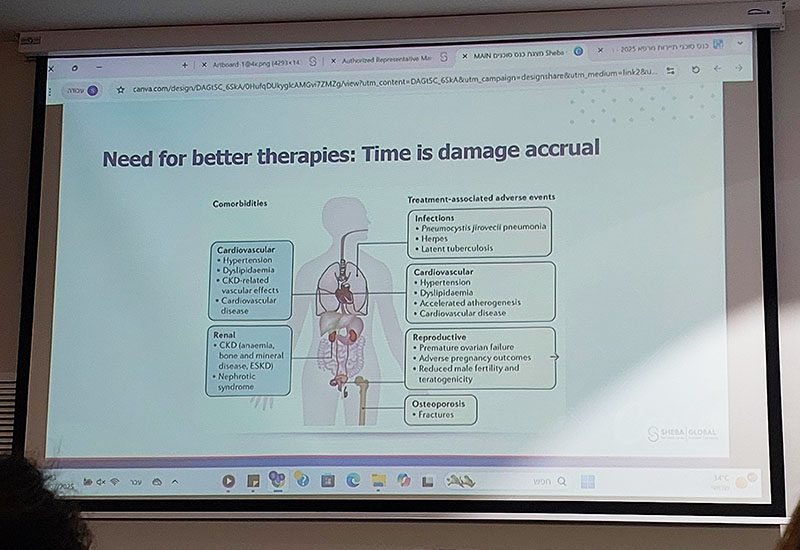
These treatments can be effective at inducing remission, but relapses are common, and long-term immunosuppression carries serious side effects. For patients with recurrent or refractory disease, options are limited — and the risk of irreversible organ damage increases over time.
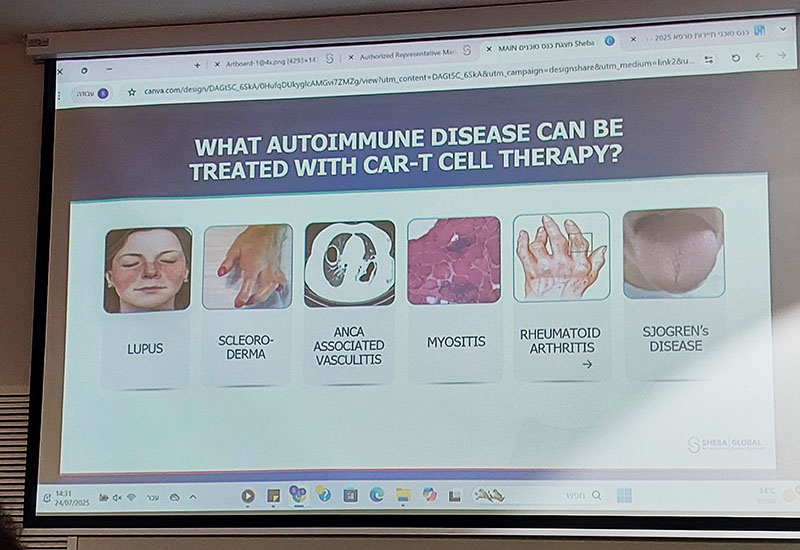
CAR-T Therapy – A New Approach to Autoimmune Vasculitis
CAR-T cell therapy for ANCA-associated vasculitis is an innovative, targeted treatment that aims to stop the disease at its source.
The process involves:
- Collecting the patient’s T-cells
- Engineering them to identify and eliminate harmful B-cells producing ANCA autoantibodies
- Reinfusing these modified T-cells to “reset” the immune system
By removing the B-cells driving vasculitis, CAR-T therapy has the potential to induce deep, long-lasting remission — without the need for continuous high-dose immunosuppressants.
Why CAR-T for ANCA Vasculitis?
B-cell depletion is already a proven strategy in AAV (as seen with rituximab), but CAR-T therapy takes it a step further, often achieving more complete and durable elimination of pathogenic B-cells.
Potential benefits include:
- Longer remission periods with reduced relapse rates
- Improved kidney and lung function in affected patients
- Reduced dependency on steroids and immunosuppressive drugs
- Better quality of life with fewer treatment side effects
The CAR-T Program for Vasculitis in Israel
Sheba Medical Center — a global leader in advanced medical innovation — is conducting a pioneering CAR-T program for ANCA-associated vasculitis as part of its initiative for severe autoimmune diseases.
The program is led by world-class specialists in rheumatology and immunology who combine cutting-edge research with compassionate, patient-centered care. International patients are welcome, with medical eligibility determined after a thorough evaluation.
Early intervention is critical: once severe organ damage has occurred, it may not be reversible. Treating vasculitis before such damage can significantly improve long-term outcomes.
Who May Qualify?
CAR-T therapy may be considered for patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis who:
- Have persistent or severe disease despite standard and biologic treatments
- Show significant organ involvement (e.g., kidneys, lungs, nerves)
- Are medically stable enough to undergo treatment in Israel (typical stay: 8–10 weeks)
Begin the Evaluation Process
If you or someone you love is facing ANCA-associated vasculitis that has not responded to standard treatments, CAR-T cell therapy in Israel could be a life-changing option.
Contact us today to learn more about eligibility, the treatment process, and how Israel’s CAR-T programs for vasculitis are giving new hope to patients worldwide.
Publication date: August 2025










