China has emerged as a leading player in CAR-T technology, boasting the highest number of clinical trials globally. Coupled with its relatively low treatment costs, it has become a popular destination for international patients seeking CAR-T cell therapy. The therapy is available for various conditions, including Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Numerous hospitals across China offer CAR-T therapy, each providing different levels of medical treatment and customer service.
How much does CAR-T therapy cost in China?
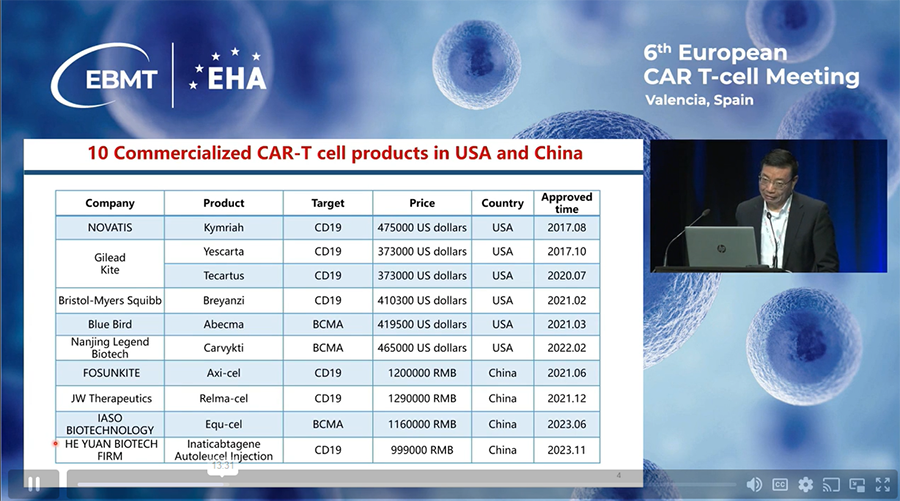
Below is a list of commercialized CAR-T cell products in China, along with their costs in Chinese RMB and the years of their approval dates. This information was presented in a lecture by Dr. He Huang from Hangzhou, China, at the 6th European CAR-T Cell Meeting in Seville, 2024.
Swipe table to see all columns| Company | Product | Price | Target | Approved time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOSUNKITE | Axi-cel | 1200000 RMB | CD19 | 2021.06 |
| JW Therapeutics | Relma-cel | 1290000 RMB | CD19 | 2021.12 |
| IASO BIOTECHNOLOGY | Equ-cel | 1160000 RMB | BCMA | 2023.06 |
| HE YUAN BIOTECH FIRM | Inaticabtagene Autoleucel Injection | 999000 RMB | CD19 | 2023.11 |
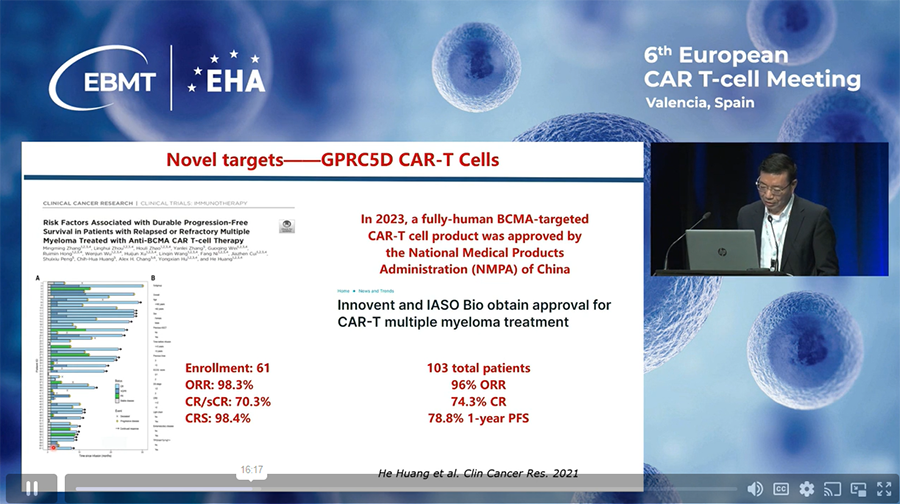
Is CAR T-cell therapy available in China for multiple myeloma?
China has developed a few CAR-T cell therapies for treatment of Multiple Myeloma. One of them is presented below.
Source.
What are the major challenges in CAR T-cell therapy in China?
International patients considering treatment in China should be mindful of certain aspects:
- Treatment Eligibility and Protocol: Being eligible for CAR-T therapy often requires the patient to have undergone at least three lines of previous treatments, among other criteria. Institutions considering a patient for treatment should meticulously review the patient's medical documents from their home country prior to arrival, ensuring the case meets the specific criteria for CAR-T therapy.
- Approval of Treatment: Ascertain whether the CAR-T therapy offered is a commercially approved treatment recognized by the FDA or if it's part of a clinical trial. Additionally, clarify whether the approval is from the American FDA or its Chinese counterpart FDA.
- Blood Supply: Understand that all hospitals in China receive blood units from the central blood bank. Seasonal blood shortages can occur, posing significant risks, especially for blood cancer treatments like Lymphoma, Leukemia, and Myeloma, where blood products are crucial.
- Language Barrier: Language can be a significant obstacle, as most hospital staff and the general population in China do not speak English. Medical reports, instructions on medical equipment, and other essential information are typically in Chinese, which can lead to misunderstandings and complications.
International patients should thoroughly investigate these factors to make informed decisions about pursuing CAR-T therapy in China.